INR that has fallen sharply this year on the back of many factors would see relief on easing trade war tensions. China has sent out feelers that it would lower its trade surplus with the US by USD 200 billion and this is leading to a temporary pause in tariff wars. Markets were on a risk aversion mode on trade war tensions and this would lead to risk aversion falling, which is positive for INR and other EM currencies.
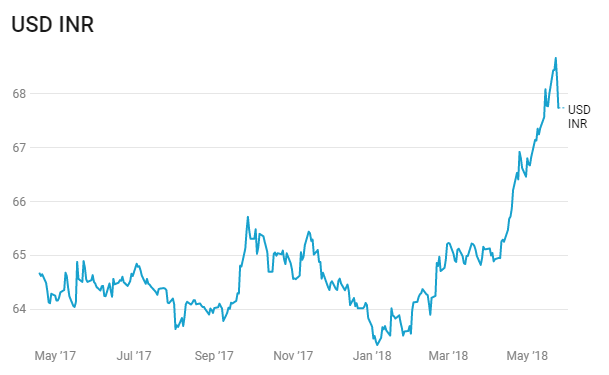
INR fell below 68 level against the USD last week and is currently trading at levels of 68.1 against the USD, down by 0.99% week on week. The rupee came under pressure last week as crude oil prices surged to USD 80/bbl coupled with higher USD demand. Fed rate hike expectation is pushing 10-year UST yields higher and underpinning the demand for USD, currently 10 Year UST yield is at 3.06%, higher by 9 bps on weekly basis.
The rupee is among the worst performing Asian currencies, which has now weakened 6.2% in 2018, as higher crude oil prices is fuelling worries of rising inflation and boosting expectations for a rate hike by RBI. The g-sec yields are factoring in rate hikes by the RBI as 10-year G-sec yields are trading at 3-year high levels of 7.83%.
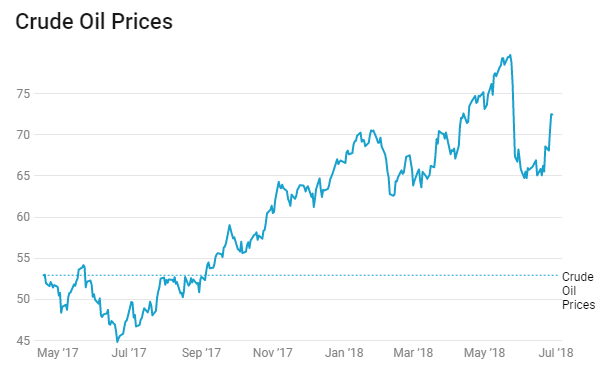
The price of oil has hit its highest level since November 2014, reaching USD 80/bbl , as geopolitical fears cause concerns to rise over potential disruption to supplies. The U.S. Energy Information Administration reported on Wednesday that crude supplies declined by 1.4 million barrels for the week ended 11th May.
USD ended the week higher amid surging bond yields and upbeat U.S. economic data. Upbeat U.S. economic data released in the recent past is making a case for faster pace of Federal Reserve rate hike. Rising UST bond yields are clearly factoring in higher interest rateS in U.S. The widening interest rate gap between the U.S. and other developed economies is making USD more appealing to global investors. USD Index (DXY), which tracks the movement of the USD against six major currencies, rose by 1.19% on a week on week basis and is at a level of 93.64.
USD started the week on a flat note after softer than expected consumer inflation data that curbed expectations for a third-rate hike by the Federal Reserve later this year. However, USD started its rally on Tuesday after the release stronger than expected U.S. retail sales report.
U.S. Commerce Department reported that while retail sales rose 0.3% in the month of April the previous months figure was revised up to 0.8% from a previously reported 0.6%. Core retail sales rose 0.3% in the month of April and March figure was revised to 0.4%, from 0.2% previously. The data pushed U.S. Treasury yields higher, with the yield on 10-year U.S. Treasury rising to 3.08%, the most since early 2014, on rising inflation expectations.
The Empire State manufacturing index rose in the month of May, to a reading of 20.1 from 15.8 in April against the expectation of 15.10.
U.S. Commerce Department reported on Wednesday that U.S. homebuilding fell 3.7% to an annual rate of 1.287 million units in April, against the expectation for a 0.7% decline. The report also highlighted a 1.8% rise in building permits to a rate of 1.347 million units, against the expectation of a 2.3% decline.
U.S. industrial output rose 0.7% in April.
U.S. Department of Labour on Thursday reported that the number of individuals filing for initial jobless benefits in the week ended 12th May rose by 10,000 to 222,000 from last week’s claim of 211,000 and against the expectation of a rise of 4,000 to 215,000.
Asian currencies were largely down last week against the USD. Australian Dollar depreciated by 0.42%. New Zealand Dollar depreciated by 0.89%. Japanese Yen depreciated by 1.25% against the USD and appreciated by 0.18% against the Euro. South Korean Won depreciated by 0.76%, Philippines Peso depreciated by 0.01%, Indonesian Rupiah depreciated by 1.38%, Indian Rupee depreciated by 0.99% against the USD and appreciated by 0.37% against the Euro, Chinese Yuan depreciated by 0.72% against USD, Malaysian Ringgit depreciated by 0.57% and Thai Baht depreciated by 0.84%.
Weekly Global Bond Market Analysis
US 10-year benchmark bond yields rose by 9 bps, 10-year UST yields hit 3.12% briefly, its highest level since 8th July 2011, while 30-year UST yields hit its highest level since 3rd October 2014.
UST yields are rising after strong US sales data and unemployment data. Initial claims for state unemployment benefits rose 11,000 to a seasonally adjusted 222,000 for the week ended May 12.
The latest number suggest labour market is almost reaching towards full employment. The tight labour market is signal that economy is healthy and demand for the workers is huge. When workers are in demand, an employer will have to pay more for their services which can increase inflation going forward.
Retails sales is also showing improvement and market now pays more attention to retail sales and average hourly earnings as clues to when record low unemployment rates will lead to inflationary pressures.
Emerging economies 10-year benchmark bond yields largely rose last week.
Indonesia 10-year benchmark bond yields rose by 7 bps after Bank of Indonesia rose interest rate for the first time since 2014, Bank of Indonesia raised the 7-day reverse repurchase rate by 25 basis points to 4.50%. Central bank raises its interest rate to protect its currency from falling, which has remained under pressure due to the spike in US bond yields, oil prices increase.
China 10-year benchmark bond yields rose by 1 bps, China economic momentum broadly held up in April with industrial production exceeding forecasts, Industrial output rose 7% in April 2018 from a year earlier, Industrial output was at 6% in March 2018.
Brazil 10-year benchmark bond yields rose by 45 bps, Economic activity in Brazil contracted more than expected in March. The central bank economic activity index fell 0.74% in March 2018, market forecast for 0.10% fall.
US high-yield bond yields rose by 4 bps to 6.28% and Eurozone high-yield bond yields rose by 3 bps to 3.07%.